Cost-effective IP Strategies: Spotting Novelty in Your Inventions
Dr Catrina Carroll, Strategy Leader, Collaborative R&D and Licensing, MDC
13 June 2024
This blog focuses on creating cost-effective Intellectual Property (IP) strategies and spotting novelty in your inventions by doing work at an early stage ‘in-house’ before you engage with external IP or patent counsel.
Why is Intellectual Property Important?
IP provides legal protection and business benefits:
- Protection – safeguarding your innovation against unauthorised exploitation and use
- Differentiation – to set your product apart from competitor offerings
- Business growth – IP can help create new revenue streams
- Business valuation – creates value in the business and helps attract investors
- Brand identity – IP can protect distinctive logos, names and designs
Different Types of IP Protection
Patentability: Conditions for Patent Eligibility
To be granted a patent, an invention needs to show certain characteristics:
- Novel – an invention that has not been previously made public in any form in any territory before the patent application is filed
- Non-obvious – the invention should not be obvious to someone with knowledge and expertise in the field, for example, a research assistant or a PhD. This criterion clearly has potential to be a ‘grey area’, but generally, it means that the invention should not be something that could be easily conceived
- Utility – the invention must have some industrial application, and you will need evidence to show it could be used
Other important factors include meeting the requirements to establish inventorship, ownership and the freedom to operate.
Cost-effective Patenting: Mastering Patent Databases and Prior Art Searches
The are many free databases available to anyone who needs to establish that their invention is genuinely patentable.
WIPO Patentscope – the World Intellectual Property Office Patentscope gives access to international Patent Co-operation Treaty (PCT) applications in full text on the day of publication. It also features a powerful search engine to navigate patents from multiple jurisdictions, and allows searches based on chemical structures. The site offers a host of useful additional information on patenting.
Global Dossier – this is provided by the five major Intellectual Property Offices (IP5). Its aims are to enable the sharing of and access to dossier information of patent families, to streamline the examination process and promote transparency across the global patent system.
The Global Dossier allows you to view communications between the examiner and the assignee (or their patent counsel) for specific patents, to see how claims evolve over the process. This can be very useful if you are looking at pending patents which may affect your freedom to operate (FTO), for example.
Google Patents – includes over 120 million patent publications produced by over 100 patent offices around the world. Further resources include technical documents and books indexed in Google Scholar and Google Books, along with documents from the Prior Art Archive.
Refine Your Patent Searches
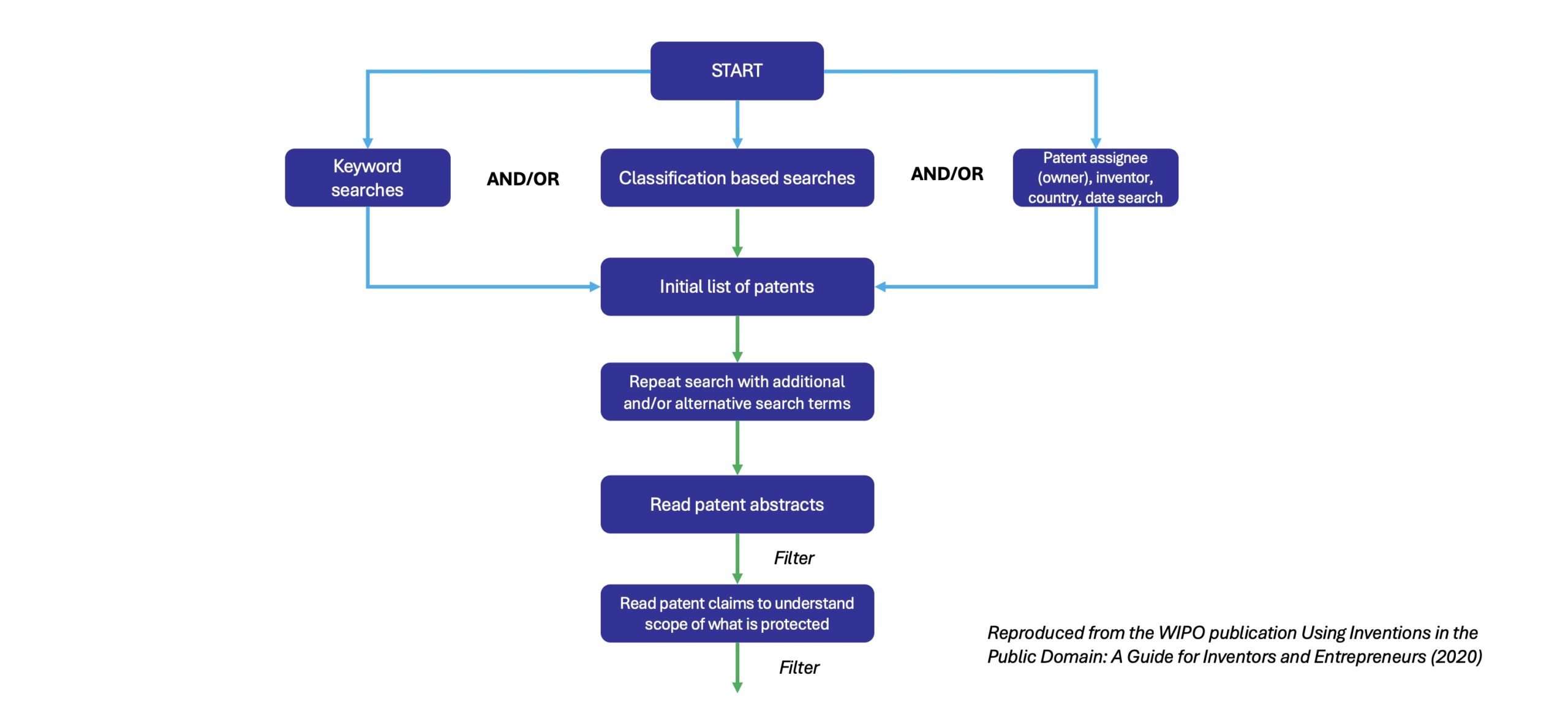
1. Searching on keywords relevant to your invention
2. Classification searches – you can refine these further to look at competitors, specific companies, inventors, countries, date searches
3. At this point you will have an initial list of patents
4. It is good practice to repeat the search using additional or alternative search terms or synonyms
5. Read patent abstracts to discover which factors will be most relevant to your invention
6. Read patent claims – to understand the scope of what is protected. This can be important in terms of FTO
7. Final list of relevant patents – the next step from here is to start engaging with external patent counsel, to gain a professional opinion on patentability and FTO
Using AI to Help Build Your Search Criteria
AI is an extremely useful tool for this task, with the major caveat that whatever you put into the chat is usually publicly disclosed. Therefore it is important to keep your information as top level as possible, or simply use it to guide your searches.
The following is an example of how AI can be used – for instance, building a search around an in-vitro kidney organoid that could be used to test drug toxicity.
Freedom to Operate
Establishing FTO is generally a matter of understanding other people’s IP, and whether your invention will infringe their rights.
It is important to focus on active (pending and granted) patents and their claims, to ensure commercial activities do not stray into someone else’s protected IP.
Searches should be conducted in relevant jurisdictions where you are commercially active. It is also best practice to set up alerts to constantly monitor your FTO status and allow pro-active steps to be taken as the market landscape evolves. Unlike patents which are ‘set in stone’ once granted, FTO is subject to ever-changing developments as new third-party patents are filed.
Using Global Dossier to Monitor Patent Examination Proceedings
By allowing access to the communications between the examiner and the assignee, Global Dossier lets you see amended claims as they evolve, providing an effective way to monitor patents which could impact your FTO. The insights provided help you assess the strength and scope of pending claims, understand the legal arguments, and potentially identify vulnerabilities or limitations in the patent that could inform your FTO strategy.
In Summary
- Stay informed – regularly monitor patent landscapes in your field for new filings and granted patents that could affect your FTO and patentability assessments
- Engage early – conduct FTO and patentability searches as early as possible to identify challenges and opportunities
- Use professional services – consider consulting with IP professionals on FTO to make the best decisions and achieve risk mitigation
- Keep detailed records – of all your FTO and patentability search processes, findings and decision-making rationale to support future legal and strategic decisions
- Plan strategically – use insights from FTO and patentability analyses to inform business strategy – including product design, market entry strategy and IP filing priorities
Dr Catrina Carroll